Immunisations
Immunisations aim to protect people for life. They often concentrate on young children as they are more vulnerable to many dangerous infections. The childhood immunisation programme aims to protect against a number of preventable diseases, including polio, pertussis, diphtheria, measles, mumps and rubella. High rates of immunisation reduce child morbidity and mortality.
.High percentage immunisation coverage is required to achieve herd immunity, meaning that it is harder for the disease to pass between people who have not been vaccinated. The more infectious the disease, the larger the number of people who have to be vaccinated to keep the disease under control. The general threshold is considered to be 95% of the population being vaccinated to break transmission.
Across Greenwich for all of the early vaccinations, the 95% target is not met.
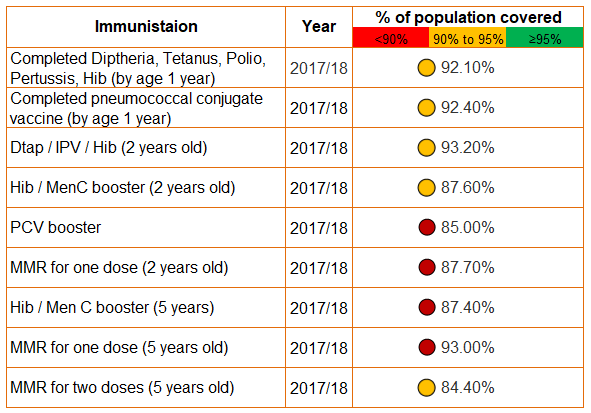
Source: Public Health Outcomes Framework
This may reflect a recording issue but is an area that requires review and intervention.